Introduction to DevOps
DevOps is a software development that bridges the gap between software developers and IT staff in a way that new features can be released more quickly and get immediate feedback. This is made possible through the use of automated CI/CD pipelines.
Why DevOps
The introduction of DevOps came into to try and do away with the traditional methods of software development methodologies, which the mostly common used ones are:
- Agile Methodology
- Waterfall Methodology.
The two methodologies each had their own advantages and disadvantages which we will brush through briefly.
Agile Methodology
To start with agile methodology, this involved a project being broken down into into various iterations and each iteration had its own phase which includes but not limited to requirements gathering, design, development, testing etc.
The challenges with this approach included:
- Lacks documentation efficiency
- Quite difficult to predict timelines for each iterations
- Not suitable for complex projects
- Increased maintainability risks
Waterfall Model Methodology
This is a straight forward methodology which is als known as top-down approach since it involved breaking the project into iterations and the next iteration could only start after the iteration before it has been completed.
The challenges of this approach included:
- Not suitable for large and complex projects
- Lack of visibility of the current progress
- The end product is only available at the end of the lifecycle
- Difficult to make changes at the testing phase
- Not suitable when requirements keep changing
Looking the challenges above, DevOps now comes in to integrate development and operations teams so as to improve collaborations and productivity.
A developer might face issues like waiting time for code deployment which DevOps solves that by continuous integration which ensures there is a quick development, testing and feedback.
Coming to operations, some of the challenges that might be faced include, difficulty in maintaining uptime of the production instances which can be solved by DevOps by usage of containerization which ensures there is a simulated environment created to run the software thus offering great reliability for service uptime.
Another challenge faced by the operations teams might be having the appropriate tools to automate infrastructure management effectively as load keeps increasing. This DevOps can help in solving it by using configuration management which organizes and executes configuration plans and manages the infrastructure effectively.
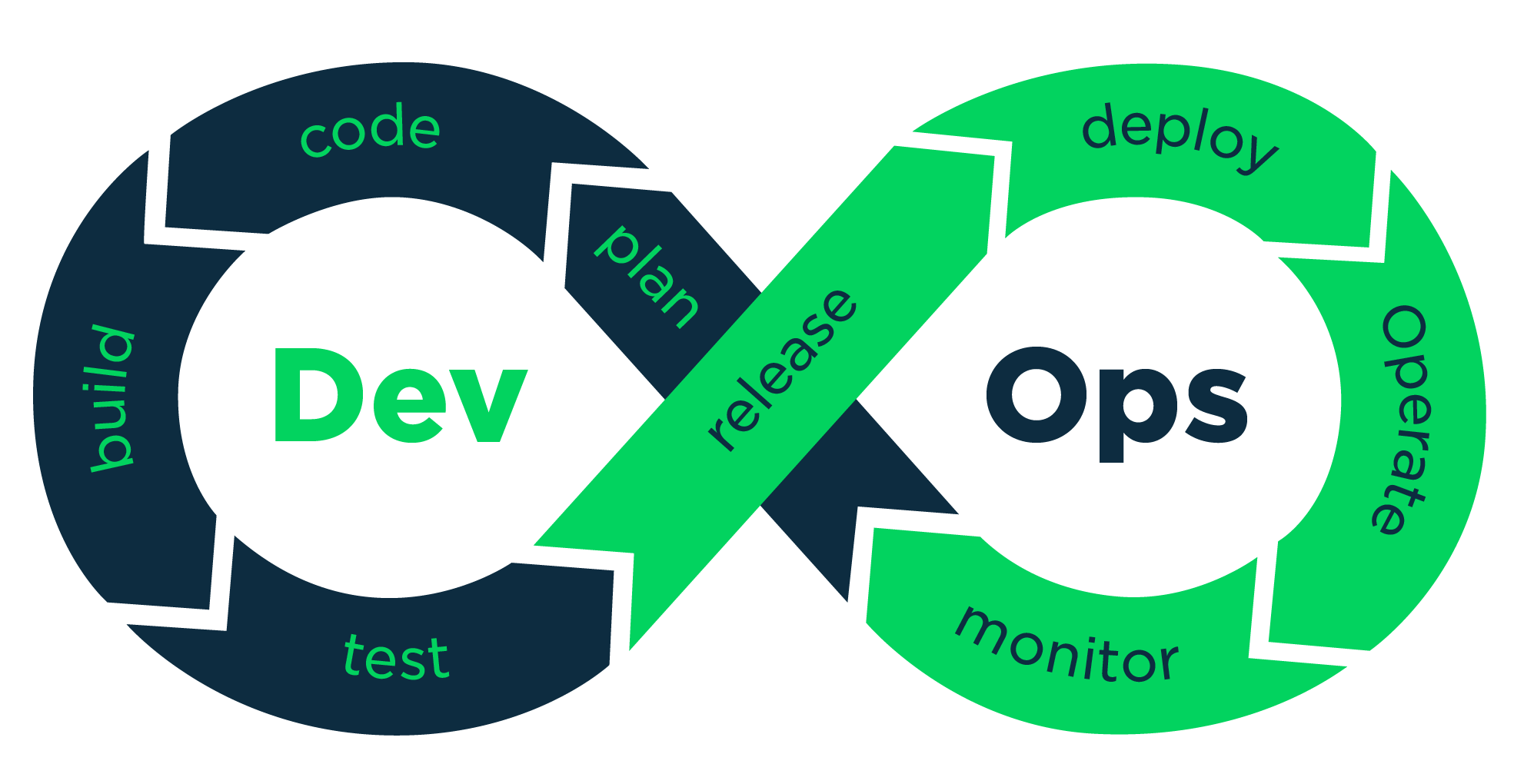
DevOps LifeCycle
The DevOps lifecycle can be categorized down into 5 phases or stages.
- Continuous Development - This phase involves planning and actual coding of the product. Some of the tools used in this phase include Mercurial and Git
- Continuous Integration - This phase involves committing the changes made to the source code more frequently, this mostly is done daily though other may prefer doing it weekly. Tools used in this phase include TeamCity, Jenkins, Travis etc.
- Continuous Testing - This phase involves testing the development product to ensure it is working as required and is bug free. Tools used in this phase include Selenium, Jenkins etc
- Continuous Deployment - This phase involves deployment of code to the production environments. Tools used in this phase include ansible, puppet for configuration management and docker for containerization.
- Continuous Monitoring - This phase involves monitoring the performance of your product. This has to be done continuously as it as a critical phase. From this you will be able to get proper metrics about the use of the product and how users are interacting with it. Tools used here include Nagios, New Relic etc.
Continuous Development: Version Control with Git and Github
In continuous development, one of the tools used is git.
Git is a distributed version control tool that supports distributed non-linear workflows by providing data assurance for developing quality software.
Most developers have adapted the use of version control as it helps keep tracks of the changes in your code and one can revert to a previous state much faster. With git one can be able to see who did changes to a particular file and what he/she did. This helps in proper tracking of changes.
For a huge project that requires collaboration between different developers, git also comes in handy as it enables collaborators to contribute to a shared repository.
Github on the other hand is a code hosting platform for version control collaboration. This allows you to host a central repository on a cental server that can be accessed bu any other team member working on the same project. Other code hosting platforms include gitlab, bitbucket etc.
Some of the top git commands commonly used include:
- git config - this is used to set the username and email to be used when make commits.
- git init - this is used when you want to start or initialize a new repository.
- git clone - this is used when you want to pull a remote repository to a local machine.
- git add - this is used when you want a file to the staging area.
- git status - this is used to list all the files that have to be committed.
- git commit - this is used when you want to commit the changes you have made to your repository.
- git push this is used when you want to push your changes from a local instance to a remote repository on a given URL.
- git pull - this is used when you want to get changes from a remote repository to your local machine.
Continuous Integration with jenkins
Jenkins is an open source automation tool built to help in continuous integration process. It is used to build and run tests on a software continuously thus enabling developers integrate new changes much easily and users also being able to see the recent changes much faster.
For the entire process to be a success a pipeline has to be built. A pipeline is a collection of jobs that brings the software from version control into the end-product consumed or used by users through an automated manner.
Building CI/CD Pipelines with Jenkins
To build a CI/CD pipeline in jenkins you can follow the below steps:
- Log into jenkins and select New Item from the dashboard.
- Enter the name of the pipeline and and select pipeline project and click OK.
- Scroll down to the pipeline and choose of you want a declarative pipeline or a scripted one and choose the respective option that works for you.
- Within the scripts, the path is the name of the jenkinsfile that is going to be accessed from your SCM to run, click apply and save.
Continuous Testing with Selenium
Selenium - is an open source tool that is used for automating the tests carried out out on web browsers.
Selenium is mainly comprised of of a suite of tools whish include:
- Selenium IDE - this allows a user to record and playback the scripts.
- Selenium RC - this is an HTTP proxy server
- Selenium webdriver - this is a browser automation tool that accepts commands and sends them into a a browser. This is the commonly used one.
- Selenium Grid - this is used to run tests on different machines against different browsers in parallel.
Continuous Deployment with Puppet
Puppet is a configuration management tool that is used for deploying, configuring and managing servers. It uses a Master-Slave architecture.
Puppet used declarative model-based approach for Infrastructure automation. This enables puppet to define infrastructure as code and enforce system configuration with programs.
In puppet we have files called manifests which is used to describe the desired state of the system and describe how you should configure your network and operating systems resources. These manifest files are then compiled into catalogs which is then applied to its corresponding node to ensure that configuration of the node is correct across the infrastructure.
Containerization with Docker
Docker is a platform that packages an application and all its dependencies together in the form of containers. This ensures that the application can work in any environment.
There are three important terms that are you are required to know when working with docker:
- Dockerfile - this is a text document that contains all the commands that a user can call on the command line to assemble an image.
- Docker image - this is like a template which is used to create docker containers.
- Docker container - this is a running instance of a docker image which holds the entire packages needed to run the application.
Some of the common docker commands include:
- docker pull - this is used to pull images from the remote docker hub.
- docker run - this is used to create a container from an image.
- docker exec - this is used to access the running container.
- docker stop - this is used to stop a running container.
- docker kill - this is used to kill the container by stopping its execution.
- docker commit - this is used to create a bew image of ab edited container on the local system.
- docker push - this is used to push an image to the docker hub repository.
- docker build - this is used to build an image from a specified docker file.
Continuous Monitoring with Nagios
Nagios is used for continuous monitoring of systems, applications and processes. In the event of a failure nagios can send a notification alerting the technical staff for immediate remediation process.
Nagios runs on a server usually as a daemon or a service. With nagios one can view the status information on the web interface or you can choose to receive email or SMS notifications if something happens since nagios behaves like a scheduler thus will run scripts at certain moments.